Are you grappling with the complexities of securing and monitoring your Internet of Things (IoT) devices, particularly those veiled behind firewalls? Effectively managing IoT devices behind firewalls is a critical, multifaceted challenge that demands innovative solutions and a proactive security posture.
The rise of interconnected devices has revolutionized industries, from smart homes to industrial automation. However, this proliferation of IoT devices has also introduced a new frontier for cybersecurity threats. These devices, often deployed in remote or difficult-to-access locations, are vulnerable to a range of attacks. Securing and managing these devices becomes even more challenging when they are located behind firewalls, which are designed to protect internal networks from external threats. Firewalls, while essential for network security, can also complicate the process of monitoring and managing IoT devices. The challenge lies in finding solutions that allow you to monitor these devices effectively without compromising the integrity of the firewall.
The core issue stems from the fundamental nature of firewalls, which are designed to control the flow of network traffic. They typically operate by allowing only pre-approved traffic to pass through. This can make it difficult to establish direct connections to IoT devices behind a firewall for monitoring, diagnostics, or remote management. Traditional monitoring techniques, such as directly accessing devices via their IP addresses, often fail. The challenge is compounded by the fact that IoT devices often lack publicly reachable IP addresses, adding another layer of complexity to remote management. The goal is to balance the need for accessibility with the paramount importance of maintaining robust security.
Several strategies and technologies can be employed to overcome these challenges. Understanding the concepts of firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and remote access solutions are essential for any organization. Effective monitoring requires more than just visibility into device status; it necessitates the ability to diagnose issues, troubleshoot problems, and ensure optimal performance. The ideal solution should provide a comprehensive view of the entire IoT ecosystem, incorporating real-time data, historical trends, and proactive alerts. The approach should be tailored to the specific requirements of the IoT deployment, taking into account factors such as the type of devices, the sensitivity of the data, and the overall security objectives.
A firewall for IoT devices provides a protective barrier between these devices and the external network, such as the internet or other local networks. The firewall acts as an effective security measure to control and monitor the incoming and outgoing traffic to and from IoT devices. An essential component of IoT security is the IoT firewall, which plays an important role in shielding interconnected devices from potential cyber threats.
The primary function of a firewall in an IoT context is to safeguard the devices from unauthorized access and potential cyber threats. It analyzes network traffic and allows or blocks it based on predefined rules. These rules are typically based on factors such as source and destination IP addresses, ports, and protocols. By carefully configuring the firewall, organizations can control which traffic can reach their IoT devices, thereby reducing their attack surface. The firewall can filter malicious traffic, prevent unauthorized access attempts, and provide a layer of defense against various security threats.
However, a firewall is not a panacea. It needs to be complemented by other security measures to provide comprehensive protection. Regular security assessments, patch management, and intrusion detection systems are crucial components of a robust security strategy. Implementing these measures ensures that the IoT devices are secure and can be monitored without compromising security. A properly configured firewall is just one component of a multilayered defense strategy.
One crucial aspect of securing IoT devices behind firewalls is the implementation of secure remote access methods. A Virtual Private Network (VPN) can be a secure way to remotely connect to Internet of Things (IoT) devices, especially when these devices are behind a firewall or a private network. VPNs establish an encrypted connection between a remote user and the internal network where the IoT devices reside. This creates a secure tunnel through which data can be transmitted, protecting it from eavesdropping and unauthorized access. In more professional or industrial settings where IoT devices may be handling sensitive data or where direct remote access to devices is required, the use of VPNs is often the preferred approach. The VPN provides a secure channel for remote management and monitoring activities, such as firmware updates, diagnostics, and troubleshooting.
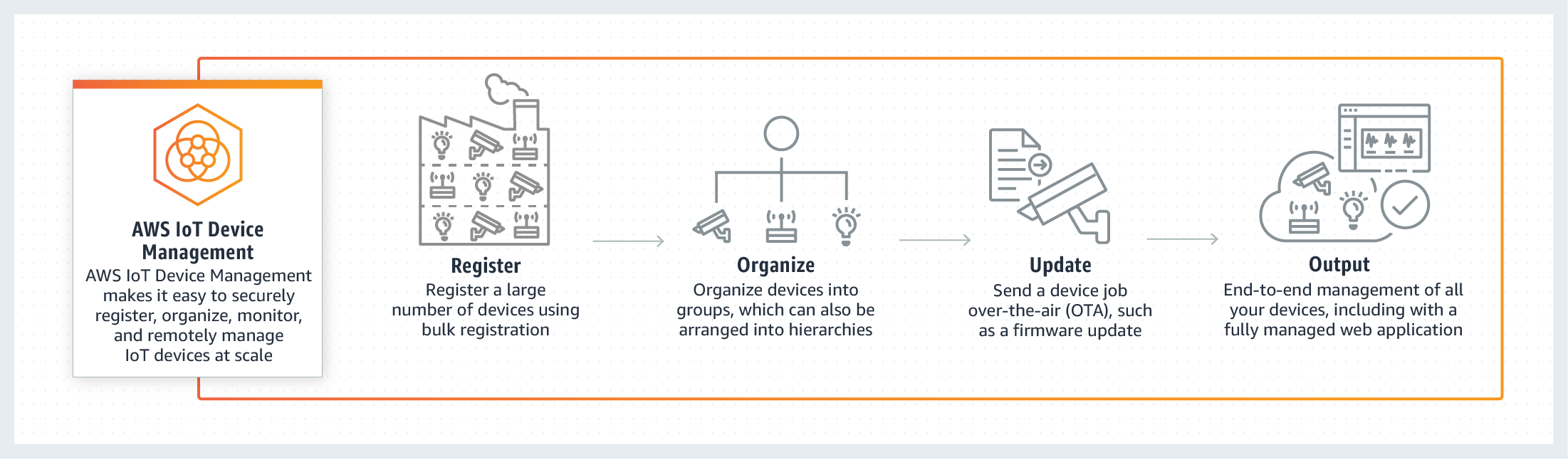
Another valuable technique is the use of device tunnels. AWS IoT Device Management supports the creation of a device tunnel a secure remote SSH session to a device installed behind a restricted firewall. This provides secure connectivity to individual devices, which you can then use to diagnose issues and solve them in just a few clicks. Using such a system provides secure connectivity to individual devices, which you can then use to diagnose issues and solve them in just a few clicks. This method simplifies the process of remote device management while maintaining a high level of security.
Remote SSH IoT behind a firewall involves using an SSH tunnel to facilitate secure communication. Every IoT device has a special IP address that helps identify it easily. The IoT devices behind the firewall can talk to servers on the internet (via the gateway router) but not the other way around. This is because you want to prevent your IoT devices from being accessed from the internet by unwanted people or hackers. It is important to remember that IoT devices do not have publicly reachable IP addresses assigned to them.
SocketXP IoT Agent, when run in IoT slave mode, acts like a local proxy server, enabling remote access to devices behind NAT routers and firewalls. You can use SocketXP to remotely connect to any IoT device behind a NAT router and firewall from an outside network such as the internet. SocketXP is a cloud-based secure remote access solution to access, manage, and debug embedded Linux devices such as IoT devices, NVIDIA Jetson, or any IoT device over the internet. The remote IoT platform allows users to remotely control IoT devices using a web browser.
Another important aspect of effective monitoring is the collection and analysis of data. Monitoring traffic patterns is crucial to obtain information about a network. You can see everything from a central point. The AWS IoT Device Management service lets you organize your devices in a structured manner. Not every firewall needs to send logs to IoT security as long as other firewalls do and their logs capture network traffic data from all the IoT devices that you want IoT security to monitor. Hover your cursor over the firewall request status icon to see if IoT security is receiving requests from firewalls for policy recommendations and IP.
Remote IoT device management platforms also play a crucial role, helping to monitor and detect uptime, troubleshoot, and resolve other issues persisting in your devices. Remote access to IoT devices also allows users to remotely control IoT devices using a web browser. Users can set up a VNC server on a Raspberry Pi and use a VNC client application on a device of choice to view and interact with the Pi's desktop from anywhere with an internet connection. This combination of remote access technologies provides a robust solution for managing and monitoring IoT devices, even when they are located behind firewalls.
One of the biggest challenges in managing and monitoring IoT devices behind firewalls is the lack of direct access. You often cannot simply connect to a device's IP address to check its status or troubleshoot issues. This necessitates the use of alternative methods to establish secure, remote connections. Remote SSH tunneling, VPNs, and cloud-based remote access solutions are invaluable tools in overcoming this challenge.
Security is a major consideration, it should be a prime focus when designing and implementing an IoT monitoring strategy. The first step is to thoroughly assess the security risks. This means identifying all potential vulnerabilities and threats to the IoT devices and the network they operate within. Consider the data sensitivity, the device's location, and the types of attacks it might be subject to. Once you understand the risks, you can develop a security strategy tailored to your specific needs. Your strategy should encompass several layers of defense. This includes firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems. Regular security audits and penetration testing can help identify weaknesses and ensure your security measures are effective. Always prioritize the implementation of strong authentication mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access the devices and data. Ensure that all firmware and software on the IoT devices are kept up to date. This can involve automated patching systems or manual updates. These are essential to patch security vulnerabilities and safeguard against malware.
When deploying IoT devices, the design must consider the network architecture. The best practice is segmenting the network to isolate IoT devices from other parts of the network. Segmentation can limit the impact of a security breach. Use a dedicated VLAN for IoT devices to isolate them from the main network. This prevents unauthorized access to sensitive data and other networked resources. The firewall should be configured with stringent rules to control the traffic flow between the IoT devices and other networks. Configure the firewall to allow only necessary traffic and block all other connections. Regularly monitor firewall logs to detect suspicious activities. Use intrusion detection and prevention systems to monitor for malicious activities within the network. If any potential threats are identified, take immediate action to mitigate the risk.
The management of IoT devices involves the implementation of effective remote access strategies. In the context of firewalls, you need secure and reliable methods for remote access and management. The deployment of VPNs is a popular choice for secure remote access. VPNs create encrypted tunnels that allow you to connect to the IoT devices securely from a remote location. Choose a VPN provider that uses strong encryption protocols, such as OpenVPN or IPSec, to protect the data in transit. The other option is implementing SSH tunneling. This approach uses an SSH tunnel to create a secure connection between a remote device and the IoT devices behind the firewall. SSH tunneling allows you to access the device's command-line interface to perform maintenance and troubleshoot. This also allows you to use cloud-based platforms or remote access solutions, like SocketXP, to provide remote access to devices behind firewalls.
Effective monitoring and alerting are central to the success of any IoT deployment. You will need to establish a comprehensive monitoring strategy to ensure the devices operate optimally and that any issues are quickly addressed. The use of a monitoring and alerting system is crucial for collecting and analyzing data from your IoT devices. This will allow you to proactively identify and respond to problems. Consider monitoring metrics such as device uptime, network connectivity, CPU usage, memory usage, and the status of critical processes. The alerts can be configured to notify you of any unusual conditions, such as device outages, high CPU usage, or unauthorized access attempts. You can use cloud-based monitoring tools, such as AWS CloudWatch, to track and monitor the performance of your devices. You can also analyze the logs to gain insights into how your devices are performing.
A crucial aspect of effective management involves logging and audit trails. Implement a robust logging mechanism to capture all relevant activities on your IoT devices and the network. Logging all of the traffic to and from the IoT devices is key. Ensure that the logs are securely stored and accessible only to authorized personnel. Regularly review the logs to identify suspicious activities. You should also create comprehensive audit trails for all access attempts to the IoT devices. The audit trails will provide a complete record of who accessed the devices, when they accessed them, and what actions they performed. Use these audit trails to investigate security incidents and identify any unauthorized activities.
In summary, the strategy for monitoring and managing IoT devices behind firewalls needs to be tailored to the specific requirements of the IoT deployment, taking into account the type of devices, the sensitivity of the data, and the overall security objectives. Organizations should implement firewalls, VPNs, intrusion detection systems, and secure remote access methods to protect the devices from unauthorized access. When using firewalls, you must also establish a monitoring and alerting system to collect and analyze data from your IoT devices. The implementation of a comprehensive security strategy and a proactive approach to device management are essential for successfully deploying and maintaining IoT devices behind firewalls.
The challenges, strategies, and best practices presented here will help you safeguard your network and ensure the secure and effective operation of your IoT devices.