Is the digital world truly secure, or are we merely navigating a minefield of potential breaches? The exponential growth of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, coupled with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, demands a complete reassessment of our security strategies. The stakes are higher than ever.
The convergence of IoT and remote access presents both unprecedented opportunities and substantial risks. From healthcare to industrial control systems, the ability to remotely monitor and manage devices offers streamlined operations and enhanced efficiency. However, this convenience comes at a price: a significantly expanded attack surface. Every connected device represents a potential entry point for malicious actors, and the consequences of a successful breach can range from data theft and operational disruption to physical damage and even loss of life.
Consider the vulnerabilities inherent in healthcare IoT devices. Ensuring the security of these devices is not merely a technical challenge; it's a moral imperative. Patient data, the very lifeblood of medical care, is constantly at risk. The potential for unauthorized access to medical records, the manipulation of medical devices, or the disruption of critical care systems is a terrifying prospect. To mitigate these risks, a multi-layered approach is essential.
Essential security measures include the implementation of secure communication protocols, the mandatory use of encryption for all patient data, and the enforcement of strict access controls. Beyond these fundamental steps, organizations must continually adapt their security posture to address emerging threats. This includes the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to detect and respond to anomalies in real-time, as well as the continuous monitoring of device behavior and the timely patching of vulnerabilities.
The allure of remote access is undeniable. Today, many businesses are hiring based on qualification rather than location. The ability to manage and troubleshoot IoT devices deployed at remote sites, regardless of geographic constraints, is a game-changer. However, this convenience often clashes with the reality of firewalls and network configurations that block inbound traffic.
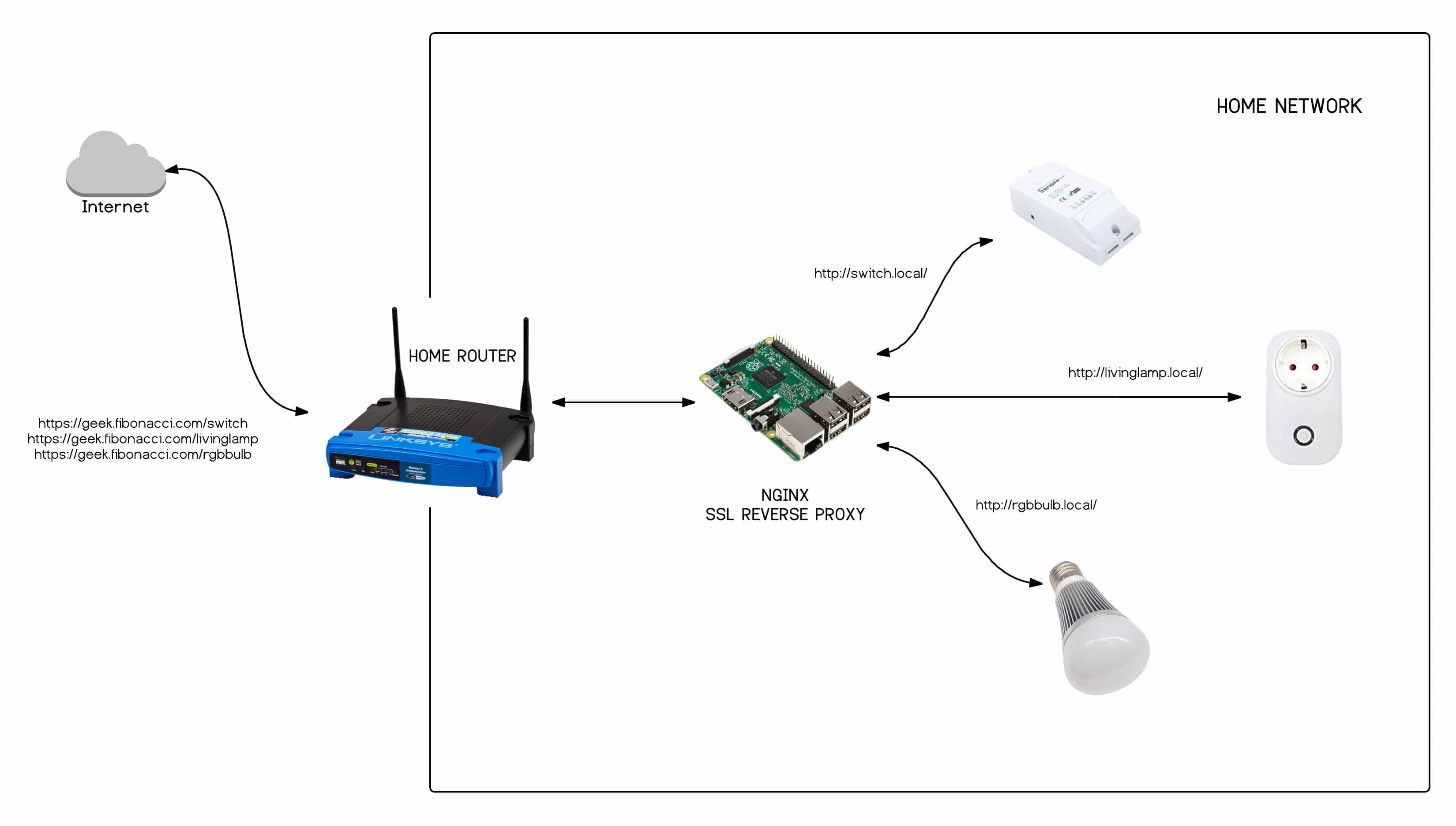
Consider the challenges faced by IT administrators and technicians when dealing with devices behind firewalls. Troubleshooting often necessitates on-site visits, which are time-consuming, expensive, and logistically complex. This is where secure remote access solutions become indispensable. These solutions enable authorized personnel to access devices securely, troubleshoot issues remotely, and perform necessary maintenance without compromising network security.
For many businesses, the costs associated with on-site interventions are increasingly prohibitive. The need for remote access has become a necessity in order to stay competitive.
The following table provides a detailed overview of the key considerations for secure remote access to IoT devices and best practices to follow:
| Area of Concern | Best Practices | Explanation | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secure Communication Protocols | Employ robust protocols like TLS/SSL and DTLS. | Ensure all communication between devices and remote access points is encrypted and authenticated. | Protects data in transit from eavesdropping and tampering. |
| Encryption | Use encryption algorithms like AES and DES. | Encrypt all sensitive data stored on devices and transmitted over networks. | Safeguards data from unauthorized access, even if a device is compromised. |
| Access Controls | Implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms. | Use multi-factor authentication (MFA), role-based access control (RBAC), and regularly review user permissions. | Limits access to authorized users and prevents unauthorized data access. |
| Password Security | Change Default Credentials | Default username and password combinations such as pi and raspberry on Raspberry Pi devices. Change the default credentials immediately. | Avoid unauthorized access to the devices. |
| Firewall Configuration | Utilize firewalls to protect access | Firewalls act as a gatekeeper to prevent unauthorized access. | Prevents unauthorized access to the devices. |
| Regular Updates | Apply software and firmware updates promptly. | Keep device software up-to-date to patch vulnerabilities. | Fix security flaws and protect against known exploits. |
| Network Segmentation | Segment your network. | Isolate IoT devices from the main network to limit the impact of a breach. | Prevents the spread of threats across the entire network. |
| Monitoring and Auditing | Implement continuous monitoring and logging. | Monitor device activity, log events, and audit access attempts. | Enables timely detection of suspicious activities and security incidents. |
| Zero Trust Architecture | Adopt a zero-trust approach. | Verify every user and device before granting access to resources. | Minimizes the impact of a compromised device. |
| Remote Access Solutions | Use tools such as Splashtop. | These tools can help organizations to manage and troubleshoot iot devices while reducing security risks. | These tools helps in maintaining the security risks. |
*Source: Example Secure Access Information
The integration of AI and machine learning (ML) in remote IoT security represents a significant leap forward. These technologies enable the automated detection of anomalies, the identification of suspicious patterns, and the proactive response to emerging threats. ML algorithms can analyze vast datasets of device activity, identify deviations from normal behavior, and alert administrators to potential security incidents. This proactive approach allows organizations to address unauthorized activity before any damage is done.
Consider the practical implementation of SSH (Secure Shell) for remote access to IoT devices. While SSH provides a secure means of communication, it is crucial to implement best practices to mitigate potential risks. This includes immediately changing the default SSH password, as the default credentials are a prime target for attackers. For instance, a Raspberry Pi comes with a default username "pi" and password "raspberry" for SSH access. These are easily found online and widely known.
Another critical step is to disable the default SSH port and configure a non-standard port to reduce the likelihood of automated attacks. Regularly monitor SSH logs for suspicious activity, such as failed login attempts, and implement rate limiting to prevent brute-force attacks. Furthermore, consider using key-based authentication instead of passwords to enhance security. This involves generating a cryptographic key pair, and using the private key to authenticate to the device, which is significantly more secure than password-based authentication.
Beyond basic security measures, organizations should explore advanced techniques such as two-factor authentication (2FA) to add an extra layer of protection. 2FA requires users to provide a second form of verification, such as a code from a mobile app or a security key, in addition to their password. This makes it significantly more difficult for attackers to gain unauthorized access, even if they have compromised a user's password.
Consider the scenario of securing a home automation system. Implementing remote access for security systems, including cameras, alarms, and access control, provides enhanced security and peace of mind. Users can remotely view surveillance footage, receive alerts, and control security features, all from their smartphones or other devices. This level of control and visibility is especially valuable in protecting homes or businesses.
Remote access to IoT devices is not solely about addressing threats; it's also about building on the capabilities that come with wireless interconnectivity. It enables efficient device management, simplifies troubleshooting, and reduces the need for on-site visits. By embracing secure remote access solutions, organizations can unlock the full potential of their IoT deployments while mitigating the associated risks.
In the context of industrial control systems (ICS) and operational technology (OT) environments, secure remote access is paramount. These environments often involve critical infrastructure and sensitive operations. Solutions like zero-trust network access (ZTNA) are designed specifically for industrial networks and harsh environments, providing secure remote access to ICS and OT assets. ZTNA solutions enforce cybersecurity controls at scale, protecting operations and preventing threats from spreading.
Implementing stronger IoT device security policies is a fundamental step. This involves establishing clear guidelines for device configuration, patching, and access management. It also includes providing regular security awareness training to employees to educate them about the threats they face and the steps they should take to protect themselves and their devices.
Some basic steps that you can take to experience better IoT device security. Utilize encryption methods like AES or DES to secure data transmitted by IoT devices. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. By combining these approaches, organizations can significantly enhance the overall security posture of their IoT environments.
Consider the financial implications. The costs associated with security breaches, including data recovery, legal fees, and reputational damage, can be substantial. Investing in robust security measures, including secure remote access solutions, is a cost-effective way to protect assets, minimize downtime, and maintain business continuity.
Ultimately, the security of IoT devices and the implementation of secure remote access are not just technical challenges; they are strategic imperatives. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, organizations must remain vigilant, adapt their security strategies, and invest in the tools and expertise necessary to protect their valuable assets and data. This ongoing commitment to security is the only way to fully realize the benefits of the IoT while minimizing the associated risks. The future of IoT security depends on the collective effort of individuals, organizations, and the security community to build a more secure and resilient digital world.