In an era defined by unprecedented connectivity, are you prepared to navigate the complex landscape of remotely accessing your Internet of Things (IoT) devices securely, particularly when they're shielded behind firewalls? Ensuring secure and efficient communication between IoT devices and your network is no longer just a technical necessity; it's the cornerstone of modern efficiency and scalability.
The relentless expansion of the Internet of Things (IoT) has woven itself into the very fabric of our lives, transforming how we interact with technology. From smart homes to industrial automation, the proliferation of connected devices offers unparalleled convenience and efficiency. However, this convenience comes at a price: the imperative to secure these devices, especially when connecting them behind firewalls. This guide serves as a comprehensive roadmap, designed to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to overcome the challenges of remote access and protect your valuable IoT assets.
Let's begin with a look at the core challenges.
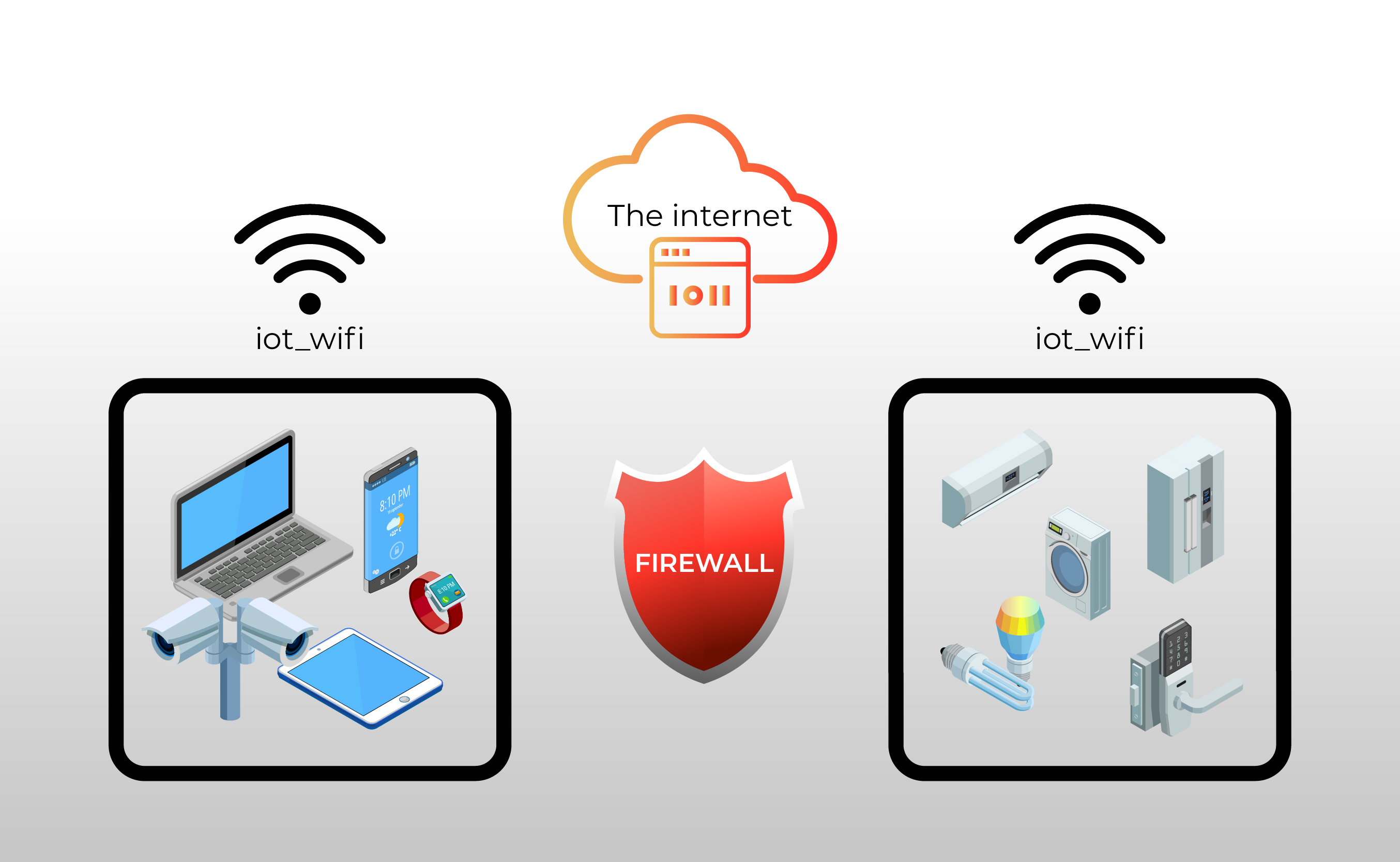
The heart of the matter lies in the fact that IoT devices typically lack publicly reachable IP addresses. They reside within private networks, behind the protective barrier of a firewall, which by design, restricts incoming connections. This means that while your devices can initiate communication with external servers (via your router), direct access from the outside world is blocked. This inherent security measure is crucial to preventing unauthorized access and protecting your devices from potential cyberattacks. But, it also creates a significant hurdle when you need to remotely access and manage these devices.
This is where the intricacies begin. The primary obstacle involves the firewall itself. Its primary function is to scrutinize all incoming and outgoing network traffic, permitting only traffic that adheres to pre-defined rules. This is achieved by analyzing the source and destination IP addresses, port numbers, and protocols. When you attempt to connect to an IoT device behind a firewall, the firewall typically blocks the connection, preventing external access. Overcoming this requires a strategic approach, carefully balancing security considerations with the need for remote access.
Several methods offer solutions. These include port forwarding, Virtual Private Networks (VPNs), and Virtual Network Computing (VNC), along with cloud-based platforms, each with its own advantages and limitations. Choosing the most suitable method depends heavily on your specific requirements, the nature of your IoT devices, and the security protocols you intend to implement.
In this guide, we will delve into each of these methods, providing clear explanations and practical guidance to help you select the most effective approach.
Methods to Connect IoT Devices Behind a Firewall: A Detailed Exploration
Connecting to an IoT device behind a firewall necessitates navigating the complex landscape of network security. The methods at your disposal each present a unique set of advantages and limitations. A thorough understanding of these options is essential to determine the best fit for your particular needs and environment.
1. Port Forwarding
Port forwarding represents a fundamental technique in network management. It allows you to redirect incoming traffic from a specific port on your router to a private IP address and port on a device within your local network (in this case, your IoT device). This enables external access to your IoT device, despite its location behind the firewall. However, port forwarding requires careful configuration.
To employ port forwarding, you must: (1) Identify the specific port used by your IoT device for communication. (2) Access your router's configuration interface (typically through a web browser). (3) Locate the port forwarding settings. (4) Enter the necessary information: the external port, the internal IP address of your IoT device, and the internal port. (5) Save your changes and restart your router.
While straightforward, port forwarding has security implications. By opening a port, you create a potential entry point for unauthorized access. Therefore, it is crucial to: (1) Use strong passwords for your IoT devices and your router. (2) Keep your router's firmware up to date with the latest security patches. (3) Consider using a firewall on your IoT device itself, as an added layer of protection. (4) Carefully monitor network traffic for any suspicious activity.
2. Virtual Private Network (VPN)
A VPN provides a secure, encrypted tunnel over the internet, effectively extending your private network. When you connect to a VPN server, your device receives a private IP address. Subsequently, any traffic from your device is encrypted and routed through the VPN, appearing as if it originates from the VPN server. This allows you to securely access your IoT devices as if you were physically present on the same local network.
To use a VPN, you'll typically:
- Choose a VPN provider: Numerous reputable providers offer various plans with varying security features and server locations.
- Install and configure VPN client software: Most providers offer user-friendly software for multiple platforms (Windows, macOS, iOS, Android).
- Connect to the VPN server: Once the software is installed, connect to your chosen server. Your internet traffic will now be routed through the encrypted VPN tunnel.
- Access your IoT devices: With the VPN connection active, you can access your devices using their private IP addresses.
VPNs offer a high level of security because they encrypt your traffic. However, you should choose a provider with a strong reputation for security and privacy. Additionally, it is vital to understand and adhere to the VPN provider's policies.
3. Virtual Network Computing (VNC)
VNC enables you to remotely control another computer or device by viewing its desktop via a graphical interface. With VNC, you establish a connection to a VNC server running on your IoT device, and then use a VNC client on your computer or mobile device to view and interact with the device's desktop from anywhere with an internet connection. This method is particularly useful for devices that have a graphical user interface (GUI).
To implement VNC, you'll need:
- A VNC server installed on your IoT device.
- A VNC client application on your remote access device (e.g., your computer or smartphone).
- A method to connect to your IoT devices network, such as a VPN, or port forwarding.
While VNC offers an intuitive way to remotely manage your devices, it's important to take necessary security precautions, such as securing your VNC server with a strong password and encrypting the connection, if the VNC client does not do so. VNC is a versatile solution but requires careful configuration to ensure security.
4. Cloud-Based Platforms (e.g., AWS IoT Core)
Cloud platforms like AWS IoT Core provide a robust and scalable solution for managing IoT devices. These platforms offer secure device connectivity, data exchange, and device management capabilities. They essentially act as intermediaries between your IoT devices and the outside world, handling complex tasks like authentication, authorization, and encryption.
To utilize a cloud platform:
- You'll typically register your devices within the platform and configure them to connect to the cloud.
- Use the platform's services for data exchange and device management.
Cloud platforms offer significant advantages, including: (1) Enhanced security: The platform handles the complexities of security, including encryption and authentication. (2) Scalability: Cloud platforms can easily accommodate a growing number of devices. (3) Management tools: They provide centralized tools for device monitoring, management, and over-the-air updates. (4) Reduced configuration: Less complex configuration compared to direct connection methods. However, using a cloud platform comes with considerations; it usually requires a subscription and involves data transfer costs. You'll also need to ensure the security of your cloud account and access to the platform.
5. RemoteIoT Platform
The RemoteIoT platform allows users to remotely control IoT devices using a web browser. Users can set up a VNC server on a Raspberry Pi and use a VNC client application on a device of choice to view and interact with the pi's desktop from anywhere with an internet connection. SocketXP also enables secure remote access to IoT devices behind firewalls and NATs, without requiring complex port forwarding. By simply installing an agent on the device and registering it with the SocketXP portal, users can access it remotely using a web browser.
To use remote iot platform, the steps are as follows:
- Users can register their connected devices individually or in bulk.
- Easily manage permissions so that devices remain secure.
- Find the device ID of the device from the socketxp portal in the IoT devices section.
This method provides a secure and efficient way to manage IoT devices, using your browser for remote access.
Considerations for Windows Environments
Managing remote IoT devices behind a firewall on Windows can be a challenging task, especially for those who are new to the internet of things (IoT) ecosystem. The same methods (VPNs, VNC, Cloud Platforms, port forwarding, and remoteIoT platform) apply to Windows environments as well, but the specifics of setup and configuration can vary.
Key Challenges in Connecting IoT Devices Behind Firewalls
While the advantages of remotely accessing IoT devices are clear, the process is fraught with challenges. Understanding these challenges is crucial for successful implementation.
1. Network Configuration Complexity
Setting up port forwarding, VPNs, or configuring a cloud platform requires a degree of technical expertise and network knowledge. Incorrect configurations can lead to security vulnerabilities or prevent remote access. The specific steps often vary depending on your router, firewall, and chosen method.
2. Security Risks
Opening ports, setting up VPNs, or using cloud services introduces potential security risks. Vulnerabilities in your router, weak passwords, or misconfigured security settings can expose your devices to unauthorized access. Protecting your devices involves diligent security practices such as strong passwords, keeping software up to date, and using encryption.
3. Device Compatibility
The method you choose must be compatible with your IoT devices. Some older or resource-constrained devices may not support VPN clients or have the processing power for encryption. Compatibility issues must be considered when choosing the correct path.
4. Network Performance Issues
The performance of remote access can be impacted by network speed, latency, and the processing power of your devices. VPNs and encryption can add overhead, potentially affecting the responsiveness of your devices. Poor network conditions can create lag or disruptions, making remote management difficult.
5. Dynamic IP Addresses
Many home internet connections use dynamic IP addresses, meaning your public IP address changes periodically. This can make it challenging to use port forwarding or VPNs, as you need to know your current IP address. Dynamic DNS services can help resolve this issue by providing a static domain name that always points to your current IP address.
6. Firmware and Security Patching
Regularly updating the firmware and security patches on your IoT devices, router, and any intermediate devices (e.g., VPN servers) is crucial. Outdated software can contain security vulnerabilities that malicious actors can exploit. Keep your devices updated to ensure the highest level of protection.
7. Firewall Rules and Configuration
Firewalls are designed to protect your network. Understanding how to configure your firewall to allow necessary traffic while maintaining security is essential. Incorrect firewall rules can block access to your devices, even when you have other connection methods configured correctly.
Troubleshooting Common Connectivity Issues
Despite taking all the necessary steps, you may encounter issues when trying to remotely connect to your IoT device. Here are some common problems and their solutions:
1. Connection Refused or Timed Out
This issue frequently arises when the target device or service is unavailable, possibly due to: (1) Incorrect IP address or port number. (2) The device is turned off or not connected to the network. (3) The firewall is blocking the connection. (4) Network configuration errors (e.g., incorrect port forwarding, VPN issues). You must: (1) Double-check IP addresses, ports, and service status. (2) Verify that the device is powered on and connected to the network. (3) Check firewall rules on both your router and your IoT device.
2. Slow Performance or Lag
This can be caused by: (1) A slow internet connection. (2) Network congestion. (3) High latency. (4) Resource limitations of the IoT device. Solutions involve: (1) Test your internet speed and check for network congestion. (2) Simplify the data being transmitted to minimize network load. (3) Ensure your IoT device has sufficient processing power and memory.
3. Authentication Failures
This usually indicates: (1) Incorrect username or password. (2) Account lockout due to repeated failed login attempts. (3) Security restrictions. To rectify this: (1) Verify username and password are correct. (2) If locked out, reset your credentials. (3) Check access control settings and ensure your account has the appropriate permissions.
4. VPN Connection Problems
This could be due to: (1) Incorrect VPN configuration. (2) VPN server issues. (3) Firewall blocking the VPN connection. (4) Incorrect authentication credentials. Resolve these issues by: (1) Reviewing your VPN configuration settings. (2) Checking the VPN server status. (3) Ensure your firewall allows VPN traffic. (4) Double-check your VPN username and password.
5. Port Forwarding Not Working
The reasons include: (1) Incorrect port forwarding settings. (2) Firewall blocking the forwarded traffic. (3) ISP blocking port forwarding. (4) Device not listening on the specified port. Resolve by: (1) Rechecking the port forwarding settings on your router. (2) Verifying your firewall allows traffic on the forwarded port. (3) Contacting your ISP to check for port-blocking restrictions. (4) Making certain your IoT device is configured to listen on the forwarded port.
6. Data Transmission Issues
These issues are related to: (1) Data loss due to poor network quality. (2) Encryption overhead which is causing data traffic overload. (3) Incompatible protocols being used by the devices. In order to solve these issues the solutions are: (1) Monitor network quality and consider using a more reliable connection. (2) Adjust encryption settings or protocol if necessary. (3) Ensure that devices are compatible with the protocols being used.
7. Device Not Registering with Cloud Platform
Possible causes include: (1) Incorrect device configuration. (2) Network connectivity issues. (3) Authentication problems. The solution is: (1) Verify the device's configuration settings in the cloud platform. (2) Ensure the device has network connectivity. (3) Double-check the device's credentials and authentication settings.
Security Considerations: Best Practices
Securing your IoT devices is paramount. Implement these security measures to safeguard your devices and data.
1. Strong Passwords
Use strong, unique passwords for all your IoT devices, router, and any associated accounts. Avoid using default passwords. Regularly update these passwords.
2. Firmware Updates
Keep your devices' firmware and software up-to-date with the latest security patches to fix vulnerabilities.
3. Network Segmentation
Consider segmenting your network by creating a separate network for your IoT devices. This limits the impact of a security breach.
4. Encryption
Use encryption whenever possible for all data transmission, especially when accessing your devices remotely. Make sure that the network uses encryption methods like WPA2/WPA3 for Wi-Fi security.
5. Authentication and Authorization
Implement strong authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication. Limit access to your devices by only granting necessary permissions. The AWS IoT core also allows you to use authentication protocols.
6. Firewall Configuration
Configure your firewall to allow only necessary traffic to your devices. Implement inbound and outbound rules. Consider using intrusion detection and prevention systems.
7. Regular Monitoring
Monitor your devices and network traffic for suspicious activity. Implement logging and alerting to identify and respond to potential security threats.
8. Physical Security
Secure your physical devices, which might include using security cameras or alarm systems.
9. Disable Unused Features
Disable unnecessary features and services on your devices to reduce the attack surface. This could mean turning off features that you do not use.
10. Security Audits
Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to assess your systems security posture.
AWS IoT Core: A Powerful Solution
AWS IoT Core, a managed cloud service, offers a powerful solution for securely connecting your IoT devices to the cloud, managing data exchange, and implementing authentication protocols. It simplifies the complexities of remote access and device management. Here's a more in-depth look at how AWS IoT Core works:
1. Device Registration and Management
You begin by registering your devices with AWS IoT Core. Each device gets a unique identity and is associated with security credentials, such as X.509 certificates, to authenticate and authorize its access to the AWS IoT platform. You can then manage these devices through the AWS IoT console, where you can monitor their status, manage their configurations, and trigger actions.
2. Secure Device Connectivity
AWS IoT Core uses the MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) protocol, a lightweight protocol ideal for resource-constrained IoT devices. MQTT provides secure, bi-directional communication between your devices and the cloud. All data is encrypted using TLS (Transport Layer Security), ensuring secure data transmission.
3. Data Exchange and Processing
AWS IoT Core allows your devices to publish data to topics, which act as communication channels. You can then subscribe to these topics to receive data from the devices. AWS IoT Core offers rules engines to process incoming data, allowing you to filter, transform, and route the data to other AWS services, such as Amazon S3 for data storage, Amazon DynamoDB for database storage, or AWS Lambda for custom function execution.
4. Authentication and Authorization
AWS IoT Core provides robust authentication and authorization features to control access to your devices and data. Each device is authenticated through its X.509 certificate, and you can use AWS IAM (Identity and Access Management) to control what resources each device can access. AWS IoT Core also offers the ability to create and manage policies that govern the permissions granted to devices.
5. Device Management Capabilities
AWS IoT Core includes device management features that allow you to remotely manage your devices. Features include: (1) Device Shadow: A device shadow represents the current state of your device. (2) Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: You can update the firmware of your devices remotely through the AWS IoT Core platform. (3) Device Job: Execute jobs on your devices to perform actions such as rebooting or configuring settings.
6. Integration with Other AWS Services
AWS IoT Core is designed to integrate with a variety of other AWS services, including: (1) Amazon S3 (for storing data). (2) Amazon DynamoDB (for data storage). (3) AWS Lambda (for custom function execution). (4) Amazon CloudWatch (for monitoring and logging). (5) Amazon Kinesis (for real-time data processing).
To Make the Most of This Guide
Remember that understanding how AWS IoT Core works, the role of firewalls in IoT security, and troubleshooting common connectivity issues is vital. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of how to securely remote connect IoT devices behind firewalls using AWS.
To make the most of this guide, we'll cover a variety of topics, including how AWS IoT Core works, the role of firewalls in IoT security, and troubleshooting common connectivity issues. You shall find the device id of the device from the socketxp portal in the IoT devices section.
Make your IoT devices to subscribe to a topic they are interested in listening, so that they could take some action like powering on a bulb. In the following example, the IoT device subscribes to the topic "office/floor1/bulb1".
Using RemoteIoT behind a firewall is a crucial skill for modern IT professionals, especially those managing IoT devices in secure networks. Managing remote IoT devices behind a firewall on Windows can be a challenging task, especially for those who are new to the Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem.